Lesson 6 - 1796 - Battle of Lodi
The Battle of Lodi and the Italian campaign that preceded it are not especially famous battles in the Napoleonic Wars. But they do illustrate some important aspects about how warfare was changing and what that can tell us about the society of the time.
As you will study later, the American Revolution from 1775 (Matu 1) and the French Revolution from 1789 (Matu 2) transformed the world. The changing nature of warfare in the late 18th century reflected those changes. These revolutionary wars were fought against the armies of the kings and they were fought for ideas, like independence and liberty. These mass revolutionary armies were made up of volunteers and represented the idea of a 'nation'. Many of the features we now recognise as modern warfare - mass armies and mass casualties, the vast scale of war, the mobilisation of whole populations - “nation in arms” - came about during the French wars. To meet the challenge, the kings and emperors of Europe had to copy the French in terms of the size and tactics of their armies and the militarisation of their societies.
One of the less obvious consequences of the move towards modern, less 'limited' warfare was the need to generate support for the war effort. The French Revolution had made governments concerned about what ordinary people might be thinking. Bigger, volunteer armies fighting for ideas needed the support of the public. Propaganda became important.
As you will study later, the American Revolution from 1775 (Matu 1) and the French Revolution from 1789 (Matu 2) transformed the world. The changing nature of warfare in the late 18th century reflected those changes. These revolutionary wars were fought against the armies of the kings and they were fought for ideas, like independence and liberty. These mass revolutionary armies were made up of volunteers and represented the idea of a 'nation'. Many of the features we now recognise as modern warfare - mass armies and mass casualties, the vast scale of war, the mobilisation of whole populations - “nation in arms” - came about during the French wars. To meet the challenge, the kings and emperors of Europe had to copy the French in terms of the size and tactics of their armies and the militarisation of their societies.
One of the less obvious consequences of the move towards modern, less 'limited' warfare was the need to generate support for the war effort. The French Revolution had made governments concerned about what ordinary people might be thinking. Bigger, volunteer armies fighting for ideas needed the support of the public. Propaganda became important.
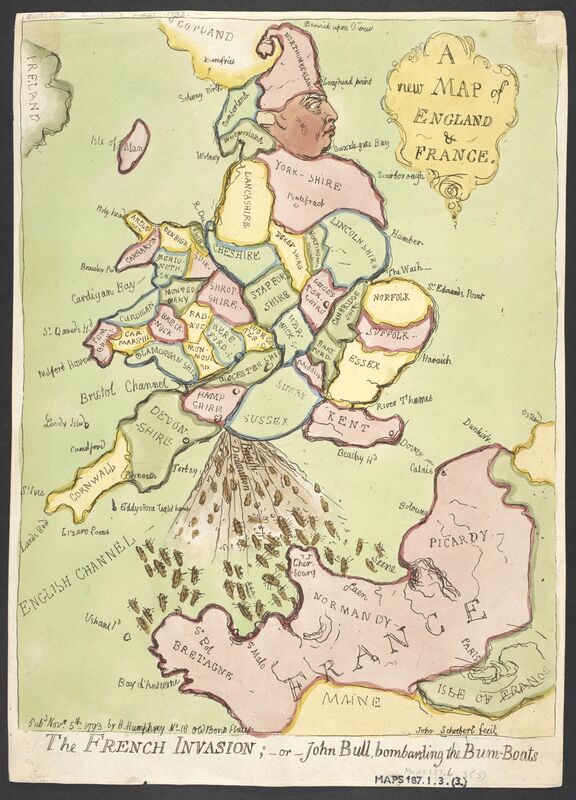
Source A - James Gillray - A new Map of England & France. The French Invasion; -or-John Bull, bombarding the Bum-Boats. 1793
|
In this cartoon map, British King George III (1738–1820) is the figure of the British mainland. He is referred to as John Bull: the brutish personification of England. The King’s night cap composes Northumberland, his left knee is Norfolk, his ankle the mouth of the Thames, his foot Kent, and his right leg the Cornish peninsula. Looking defiant, George empties his bowels on a fleet of French ‘bumboats’ (supply vessels) which ply the Channel above the face of France. His excrement showers out of Portsmouth, hub of the British Royal Navy. This crudely comic map was published when Britain was at war with France and was facing the threat of invasion. www.bl.uk/collection-items/a-new-map-of-england-and-france-the-french-invasion Question 1 (in the style of IB history - OPCVL - explanation below) With reference to its origin, purpose and content, analyse the value and limitations of Source A for a historian studying the Napoleonic wars. You should divide your answer into two sections, consider the value of the source and then the limitations. Origin refers to when, where and who produced the source. Purpose is concerned with why the source was made. Content refers to the information contained within the source. You should try and refer at least once to the origin, purpose and content in your answer. |
English cartoonist recently produced a modern version of this famous cartoon as a commentary on recent relations between the UK and France in the dispute over fishing right in the Channel.
Source B - Extract from the PBS documentary series Napoleon (2000) produced by David Grubin.
|
|
Napoleon was made possible by the French Revolution. His relatively poor Corsican background would have prevented him from being promoted so quickly in a royalist army. His revolutionary tactics on the battlefield were partly inspired by the Prussian King Frederick the Great but also by necessity. His large revolutionary army had to constantly attack because it could not be supplied other than through conquering new territory and through foraging or 'living off the land'. This inevitably meant that more civilians became innocent victims of the French armies. As we see later this year, this gradually weakened Napoleon's control over the French empire as French rule became increasingly unpopular. |
This short extract from a documentary explains the revolutionary nature of Napoleon's tactics. You can read more about the making of the film with this interview with the producer David Gruben.
|
Question 2 (in the style of IB history - OPCVL - explanation below)
With reference to its origin, purpose and content, analyse the value and limitations of Source B for a historian studying the Napoleonic wars. You should divide your answer into two sections, consider the value of the source and then the limitations. Origin refers to when, where and who produced the source. Purpose is concerned with why the source was made. Content refers to the information contained within the source. You should try and refer at least once to the origin, purpose and content in your answer. |
|
|
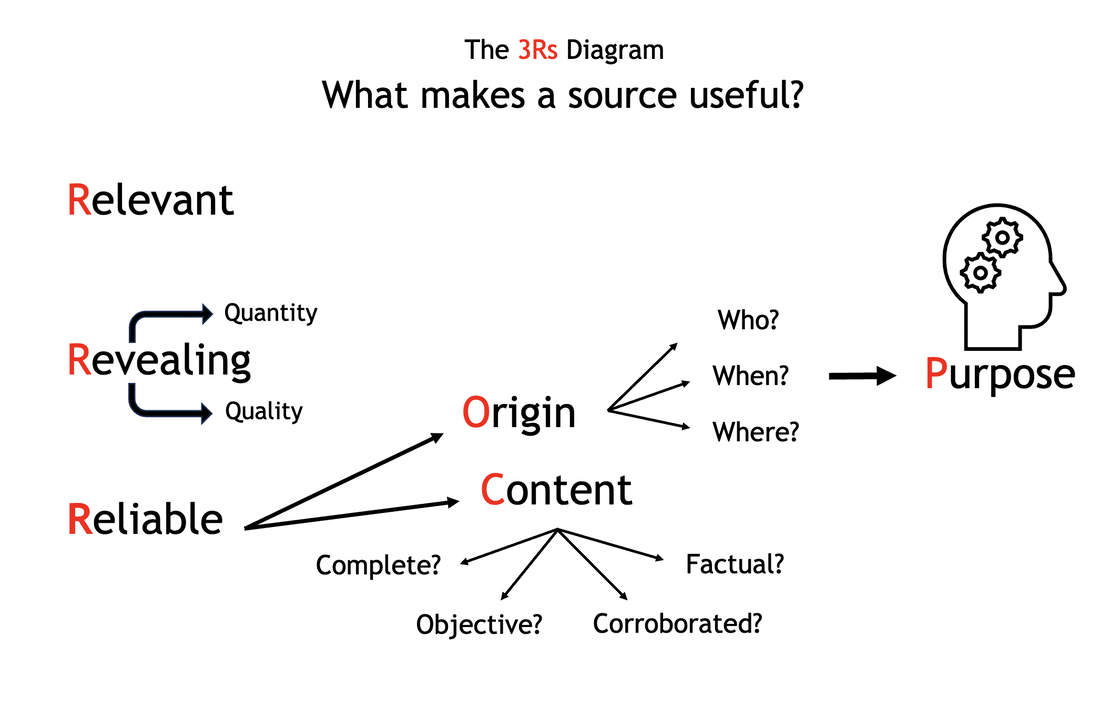
OPCVL = origin, purpose, content, value and limitations. ... is the IB history approach to source analysis. You should approach this in two stages:
Value of the source to the historian - with reference to origin, purpose and content. Limitations of the source to the historian - with reference to origin, purpose and content. |