Lesson 1 - Why was Britain the first country to have an Industrial Revolution?
|
What was the Industrial Revolution?
The Industrial Revolution was a period from the 18th to the 19th century where major changes in agriculture, manufacturing, mining, and transport had a profound effect on the socio-economic and cultural conditions starting in the United Kingdom, and then subsequently spreading throughout Europe, North America, and eventually the world. The onset of the Industrial Revolution marked a major turning point in human history. Almost every aspect of daily life was eventually influenced in some way, from where people lived and worked to how people viewed the world and their life expectations. Starting in the later part of the 18th century there began a transition in parts of Great Britain's previously manual labour and draft-animal based economy towards machine-based manufacturing. |
|
It started with the mechanisation of the textile industries, the development of iron-making techniques and the increased use of refined coal. Trade expansion was enabled by the introduction of canals, improved roads and railways. The introduction of steam power fuelled primarily by coal, wider utilisation of water wheels and powered machinery (mainly in textile manufacturing) underpinned the dramatic increases in production capacity.
Why was Europe first?
One question of interest to historians is why the industrial revolution occurred in Europe and not in other parts of the world in the 18th century, particularly China, India, and the Middle East, or at other earlier times like in Classical Antiquity or the Middle Ages. Numerous factors have been suggested, including education, technological changes (especially the Scientific Revolution in Europe), 'modern' government, 'modern' work attitudes and culture.
Some historians such as David Landes and the sociologist Max Weber credit the different belief systems in China and Europe with dictating where the revolution occurred. The religion and beliefs of Europe were largely products of Judaeo-Christianity, and Greek thought. Conversely, Chinese society was founded on men like Confucius, Lao Tzu (Taoism), and Buddha (Buddhism). Whereas the Europeans believed that the universe was governed by rational and eternal laws, in the East it was more generally believed that the universe was in constant flux and, for Buddhists and Taoists, not capable of being rationally understood.
Other recent historians like Jared Steel have suggested the physical geography of Europe and the existence of small rival nation states made all the difference. See this interesting extract and fuller version from Jared Steel's bestselling Guns, Germs and Steel and this series of documentary films.
One question of interest to historians is why the industrial revolution occurred in Europe and not in other parts of the world in the 18th century, particularly China, India, and the Middle East, or at other earlier times like in Classical Antiquity or the Middle Ages. Numerous factors have been suggested, including education, technological changes (especially the Scientific Revolution in Europe), 'modern' government, 'modern' work attitudes and culture.
Some historians such as David Landes and the sociologist Max Weber credit the different belief systems in China and Europe with dictating where the revolution occurred. The religion and beliefs of Europe were largely products of Judaeo-Christianity, and Greek thought. Conversely, Chinese society was founded on men like Confucius, Lao Tzu (Taoism), and Buddha (Buddhism). Whereas the Europeans believed that the universe was governed by rational and eternal laws, in the East it was more generally believed that the universe was in constant flux and, for Buddhists and Taoists, not capable of being rationally understood.
Other recent historians like Jared Steel have suggested the physical geography of Europe and the existence of small rival nation states made all the difference. See this interesting extract and fuller version from Jared Steel's bestselling Guns, Germs and Steel and this series of documentary films.
Why Britain?
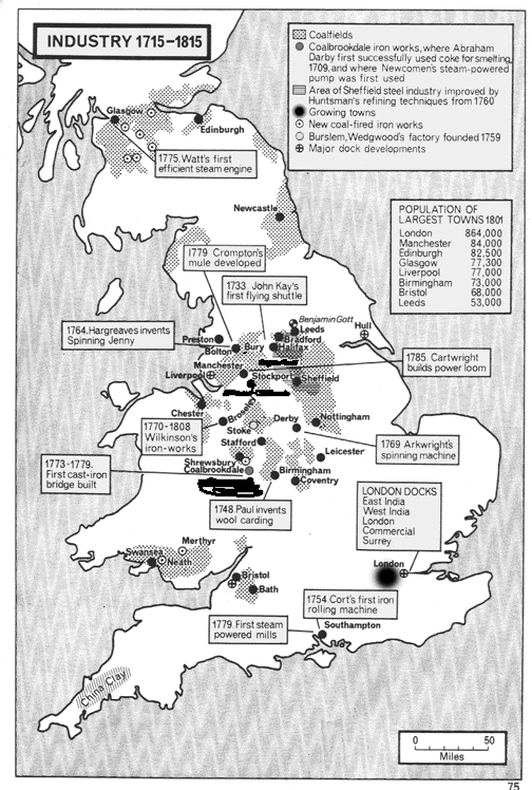
Timeline of British Industrial Development
1733: John Kay's 'Flying Shuttle' invented; it increases the speed of textile weaving machines
1767: James Hargreaves's 'Spinning Jenny' invented; it greatly increases the output per person
1769: Richard Arkwright's 'Water Frame'
1779: Samuel Crompton takes out a patent for spinning by 'mule'
1780s: 477 inventors' patents registered (in the 1710s there had been only 38) Value of exports from Britain (mostly manufactured goods) top £10 million for the first time (in the 1700s they had been less than £5 million)
1782: James Watt's rotary steam-engine invented; it enabled concentration of power away from fast-flowing streams and thus aided growth of industrial towns
1783-4: Henry Cort's 'puddling' process allowed coal, rather than charcoal, to be the main fuel used in iron refining
1786: Edmund Cartwright's power loom invented; it promises to increase speed of weaving, but is not widely introduced to textile areas until 1820s
1802: The value of exports of cotton goods exceeds those of woollen ones for the first time
Timeline of British Industrial Development
1733: John Kay's 'Flying Shuttle' invented; it increases the speed of textile weaving machines
1767: James Hargreaves's 'Spinning Jenny' invented; it greatly increases the output per person
1769: Richard Arkwright's 'Water Frame'
1779: Samuel Crompton takes out a patent for spinning by 'mule'
1780s: 477 inventors' patents registered (in the 1710s there had been only 38) Value of exports from Britain (mostly manufactured goods) top £10 million for the first time (in the 1700s they had been less than £5 million)
1782: James Watt's rotary steam-engine invented; it enabled concentration of power away from fast-flowing streams and thus aided growth of industrial towns
1783-4: Henry Cort's 'puddling' process allowed coal, rather than charcoal, to be the main fuel used in iron refining
1786: Edmund Cartwright's power loom invented; it promises to increase speed of weaving, but is not widely introduced to textile areas until 1820s
1802: The value of exports of cotton goods exceeds those of woollen ones for the first time
Nine reasons why Britain was first.
Economic historians are agreed about very little but on one point there is unanimity, no one reason by itself explains why Britain, a fairly remote group of islands in the north-west corner of Europe, became the world's first industrial nation. We can, however, identify a number of factors that gave Britain an advantage.
Economic historians are agreed about very little but on one point there is unanimity, no one reason by itself explains why Britain, a fairly remote group of islands in the north-west corner of Europe, became the world's first industrial nation. We can, however, identify a number of factors that gave Britain an advantage.
|
|
Geography: Britain is a small country with many navigable rivers, good mineral deposits (coal, iron etc.) and relatively few huge natural obstacles (mountains) to movement of trade and people. Water power, crucial for technological development, is abundant. Nowhere is very far from the sea.
Diversity: Britain has a diverse climate, enabling good-quality wheat to be grown in the south and east and animals to be nourished in western pastures. Diversity aids growing specialisation in agriculture, while Lancashire's famously mild and wet climate was helpful to the processing of raw cotton. Earlier economic development: The eighteenth century had seen remarkable advances in both trade and manufacture, resulting in rising incomes and the capacity for many people to consume manufactured goods. |
Rising population growth: Britain's population almost doubled in the course of the eighteenth century and the growth was most marked towards the end of the century. More people mean more opportunities for production and consumption.
The profitability of overseas trade and the advantage of empire: Britain had a healthy lead over European competitors in overseas trade, particularly in India and the Americas. Successes in war up to 1763 had extended this advantage. Success in war against revolutionary France helped as every other major European competitor had been economically damaged by war.
The nature of government: After the Glorious Revolution in 1688, Britain had a relatively stable government that was open to change. During the late eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries, governments were less and less likely to uphold apprenticeship regulations and other feudal restrictions on the free movement of labour.
The profitability of overseas trade and the advantage of empire: Britain had a healthy lead over European competitors in overseas trade, particularly in India and the Americas. Successes in war up to 1763 had extended this advantage. Success in war against revolutionary France helped as every other major European competitor had been economically damaged by war.
The nature of government: After the Glorious Revolution in 1688, Britain had a relatively stable government that was open to change. During the late eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries, governments were less and less likely to uphold apprenticeship regulations and other feudal restrictions on the free movement of labour.
|
Britain as an inventive society: Britain generated a huge number of innovative ideas during the eighteenth century. The famous industrial innovations - the Water Frame, Power Loom and the rest - were evidence of a much wider commitment to experiment, from which society benefited. Also new institutions, such as the Royal Society of Arts (1754), promoted innovation and diffusion of scientific and technological ideas.
Britain's advantage as a Protestant country: This explanation has its origins in the views of the German sociologist Max Weber who argued that Protestant values and lifestyles were more conducive to thrift, hard work and accumulations of money than were Catholic ones. |
|
Britain as an 'open society': Some social historians, notably Professor Harold Perkin, have laid particular stress upon the unique nature of British society. He sees a relatively liberal society open to talent in which the ablest can rise to wealth, influence and power. This is called social mobility. Also Britain's aristocracy was not a closed system; younger sons often married the heiresses of bankers and overseas traders, while very successful entrepreneurs came from humble backgrounds.
Activities
1. What reasons have been suggested to explain why Europe was the first continent to industrialise? Why is it impossible to’ know’ for certain why Europe was first?
2. This page suggests nine different reasons why the industrial revolution occurred first in Britain. Can you combine and reorganise the reasons into no more than five factors? For each factor make a big point, explain it and give an example. (PEE) Can you think of a way of dividing the reasons into just two factors? In your view, which is the most persuasive explanation for why Britain industrialised first?
1. What reasons have been suggested to explain why Europe was the first continent to industrialise? Why is it impossible to’ know’ for certain why Europe was first?
2. This page suggests nine different reasons why the industrial revolution occurred first in Britain. Can you combine and reorganise the reasons into no more than five factors? For each factor make a big point, explain it and give an example. (PEE) Can you think of a way of dividing the reasons into just two factors? In your view, which is the most persuasive explanation for why Britain industrialised first?
Extension
A good, simple explanatory essay has been produced on the History Crunch website. You could do worse at this stage than to copy both the style and content. It has a simple, clear introduction, explains the five points very clearly and provides precise facts to illustrate the points made.
Towards IB Double Diploma
In IB history you need to consider and evaluate which factors were most important to Britain's early devlopment. You need to be able argue a case. John Green clearly loves the industrial revolution - he has covered it in Crash Course lots of times - the video below focuses on why the revolution was important and why Europe was first. From what you've studied above, I think you could take him on in a debate about why Britain was first. What do you think of his explanation? Anything missing? And if you're really serious watch the video 'why did the Industrial Revolution happen here? To what extent does it confirm what you have learnt in this lesson?
A good, simple explanatory essay has been produced on the History Crunch website. You could do worse at this stage than to copy both the style and content. It has a simple, clear introduction, explains the five points very clearly and provides precise facts to illustrate the points made.
Towards IB Double Diploma
In IB history you need to consider and evaluate which factors were most important to Britain's early devlopment. You need to be able argue a case. John Green clearly loves the industrial revolution - he has covered it in Crash Course lots of times - the video below focuses on why the revolution was important and why Europe was first. From what you've studied above, I think you could take him on in a debate about why Britain was first. What do you think of his explanation? Anything missing? And if you're really serious watch the video 'why did the Industrial Revolution happen here? To what extent does it confirm what you have learnt in this lesson?
|
|
|
