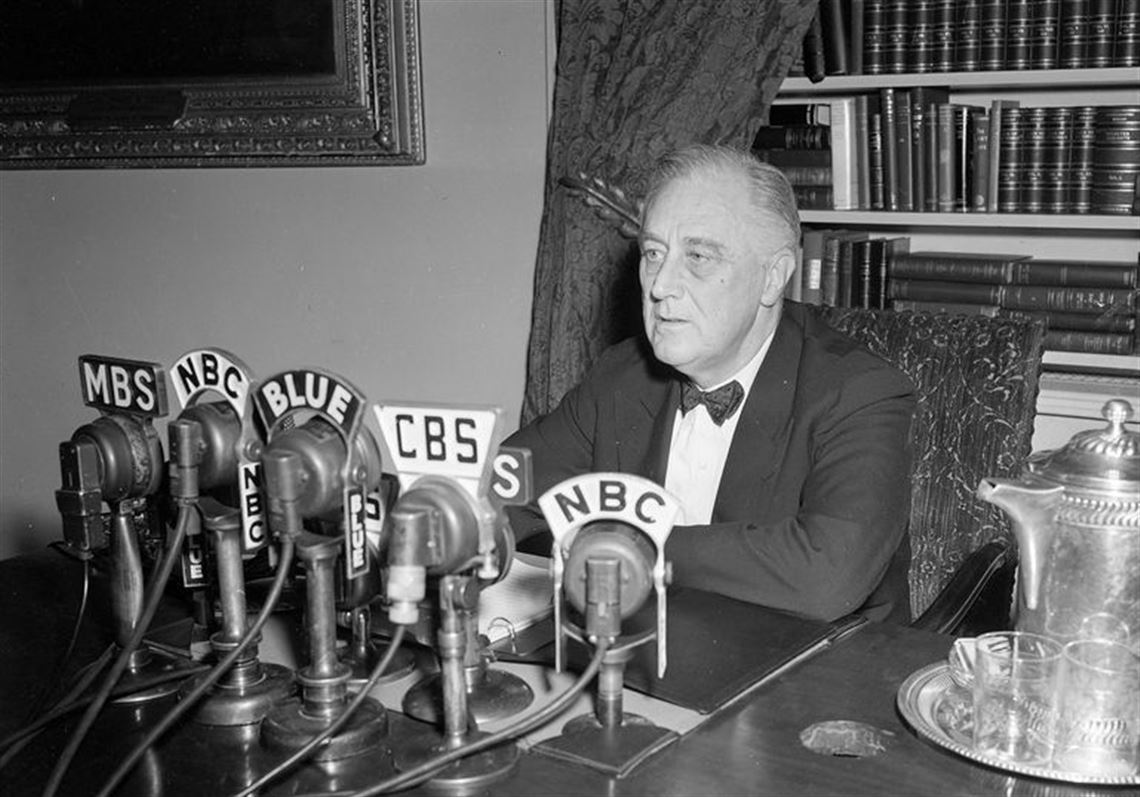
Lesson 5 - Franklin D Roosevelt and the New Deal
|
|
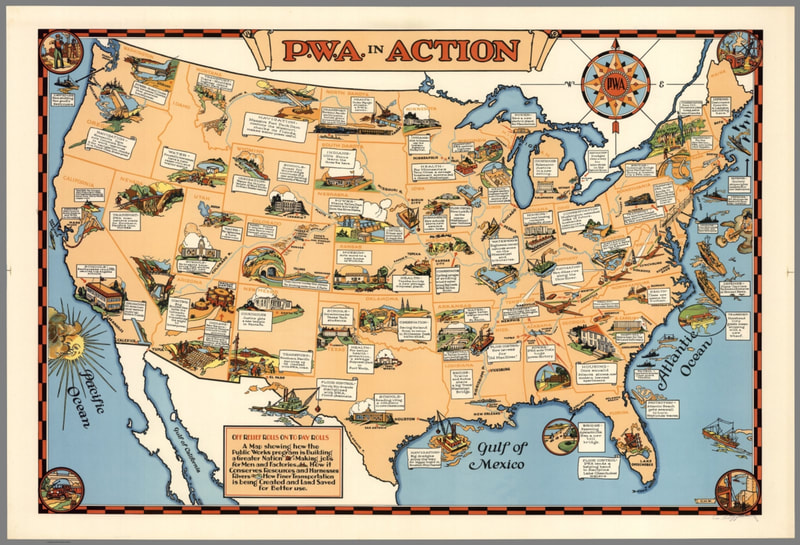
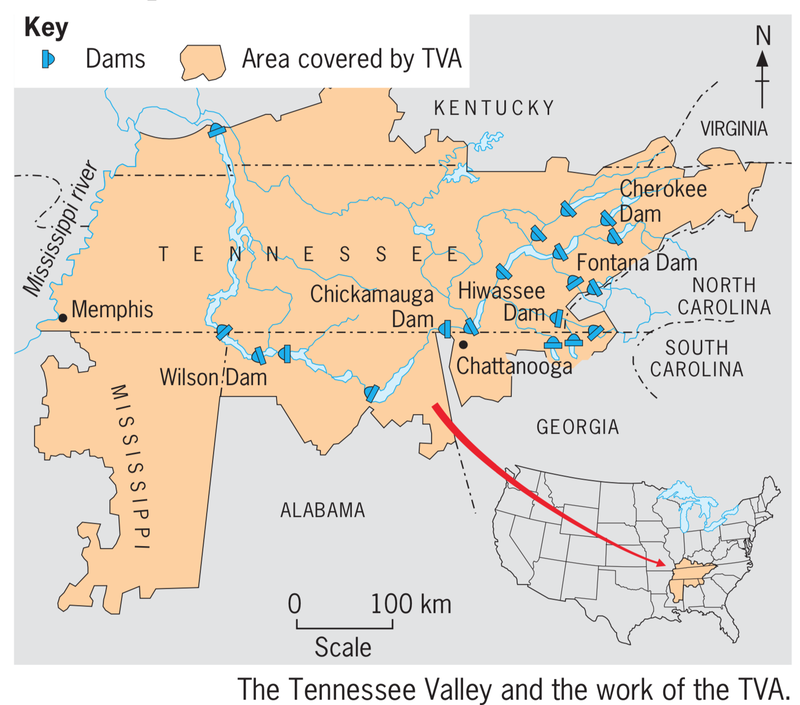
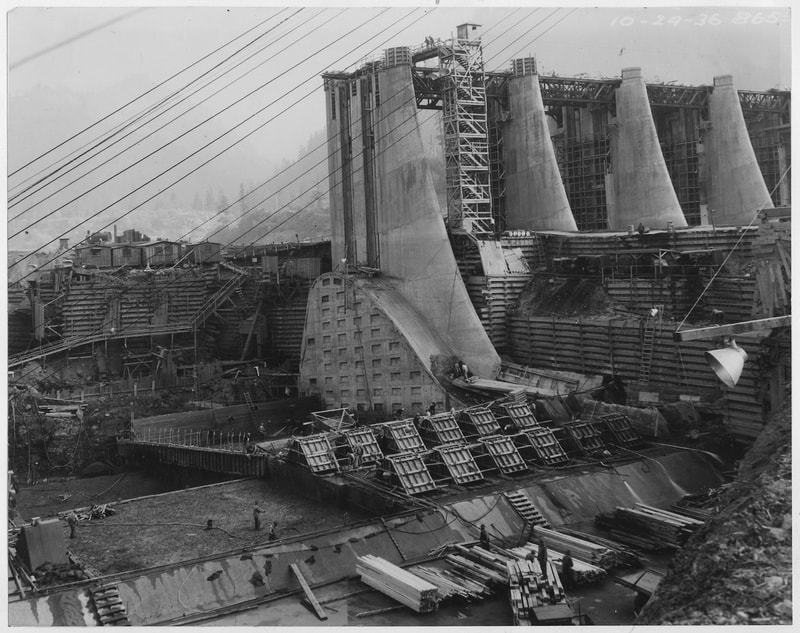
The New Deal was a series of programs, public works projects, financial reforms, and regulations enacted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the United States between 1933 and 1939. It aimed to address the economic problems caused by the Great Depression and to provide relief, recovery, and reform. The New Deal also created many public works projects, such as the Civilian Conservation Corps, which employed young men to carry out environmental and conservation projects, and the Public Works Administration (PWA), which funded the construction of public buildings and infrastructure, like bridges, roads and government buildings. |
The First New Deal - 1933-1934
The First New Deal refers to the set of programs and policies implemented by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the first two years of his presidency, from 1933 to 1935. These programs were focused primarily on providing relief to the unemployed and to farmers, and on stimulating economic recovery through public works projects and financial reforms.
The New Deal is often summed up by the 'Three Rs':
The First New Deal refers to the set of programs and policies implemented by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the first two years of his presidency, from 1933 to 1935. These programs were focused primarily on providing relief to the unemployed and to farmers, and on stimulating economic recovery through public works projects and financial reforms.
The New Deal is often summed up by the 'Three Rs':
- relief - for the unemployed and farmers through short-term federal spending
- recovery - of the economy by stimulating economic growth through federal spending and job creation to get people spending again
- reform - of capitalism, by means of regulatory legislation and the creation of new social welfare programs.
Relief |
Recovery |
Reform |
Federal Emergency Relief Act (FERA) May 12, 1933 Gave immediate help to those that needed it in the form of cash payments. |
Works Progress Administration (WPA) April 8, 1935 Repair and construction of roads, bridges, public parks, and public buildings, the WPA also paid for federal art, theater, music, theatre, and writing programs. |
Social Security Administration August 14, 1935 Provided a new federally administered system of social insurance for the aged financed through payroll taxes paid by employees and their employers. |
In reality it is actually quite difficult to consistently distinguish between the application of the 'Three R's' because many measures actually targetted two or more of the goals. But broadly speaking we can say that 'Relief' was more important at the beginning of the New Deal and 'Reform' was more important at the end. In addition, the long-term significance of the New Deal is measured in terms of the Reforms that were introduced.
Some of the key programs of the First New Deal include:
Some of the key programs of the First New Deal include:
- The Federal Emergency Relief Administration (FERA)
- The Civil Works Administration (CWA)
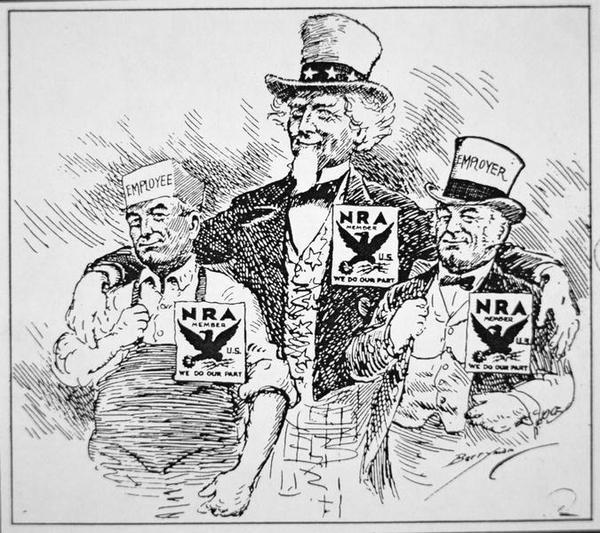
- The National Recovery Administration (NRA)
- The Agricultural Adjustment Act (AAA)
The Textbook 218-20 outlines the main features of the First New Deal and the Khan Academy provides you with the essentials that will get you through the Matu. The Digital Library of America also provides a good clear, multimedia summary.
The Second New Deal
The Second New Deal refers to the set of programs and policies implemented by President Roosevelt in 1935 and 1936, after the midterm elections. These programs built upon the programs of the First New Deal and aimed to address some of the shortcomings of those earlier policies. The Second New Deal programs were more focused on providing assistance to specific groups such as labor and farmers and on reforms aimed to address structural issues in the economy. Some of the key programs of the Second New Deal include:
See page 221. Explain why the Second New Deal was introduced and create a new table similar to that created for the first New Deal.
The Second New Deal refers to the set of programs and policies implemented by President Roosevelt in 1935 and 1936, after the midterm elections. These programs built upon the programs of the First New Deal and aimed to address some of the shortcomings of those earlier policies. The Second New Deal programs were more focused on providing assistance to specific groups such as labor and farmers and on reforms aimed to address structural issues in the economy. Some of the key programs of the Second New Deal include:
- The Works Progress Administration (WPA)
- The Social Security Act
- The Fair Labor Standards Act
- The National Labor Relations Act
- The Resettlement Administration
See page 221. Explain why the Second New Deal was introduced and create a new table similar to that created for the first New Deal.
Also consider the following:
https://www.johndclare.net/America9.htm
https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/zcrdcwx/revision/1
Extension
|
|