Lesson 3 - The Wall Street Crash and Great Depression
The Wall Street Crash of 1929, also known as the Stock Market Crash of 1929 or the Great Crash, was a major stock market crash that occurred in late October 1929. It is often considered to have been the beginning of the Great Depression.
The Wall Street Crash of 1929, also known as the Stock Market Crash of 1929 or the Great Crash, was a major stock market crash that occurred in late October 1929. It is often considered to have been the beginning of the Great Depression.
|
If you have a Netflix account, this 'explained' episode is an excellent introduction in to the origins and function of the US stock market.
https://www.netflix.com/watch/80243757 Activity 1 Read Walsh pages 211-2. Using the films and the text, briefly explain how the stock-market works and how people made so much money in the 1920s |
What caused the Wall Street Crash?
- Economic conditions: The U.S. economy had been growing rapidly in the 1920s, but there were signs of weakness beginning to appear by the end of the decade. Factors such as rising interest rates, a decrease in consumer spending, and a decrease in business investment all contributed to a sense that the economy was starting to slow down.
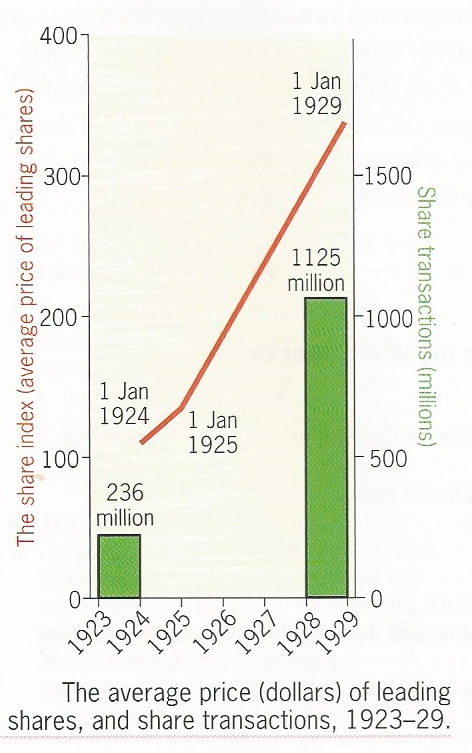
- Stock market speculation: The stock market had been rising rapidly in the 1920s. The use of leverage (borrowing money to invest in stocks) was also a factor as it amplified the effects of both gains and losses. This led to a stock market bubble, with stocks becoming overvalued and investors becoming over-optimistic about the future of the market.
- Uneven distribution of wealth: The prosperity of the 1920s had been concentrated among a small number of Americans, while many others had been left behind. This led to a lack of consumer spending power among the general population, which contributed to the economic slowdown.
- Banking failures: Many banks had invested heavily in the stock market and loaned money to those wanted to invest. There was a lack of government regulation. When the market crashed, many banks failed, which led to a loss of confidence in the banking system and further exacerbated the economic downturn.
- International factors: The crash occurred in part because of the increased instability in Europe and Republican protectionist policies made export to Europe difficult.
|
Activity 2
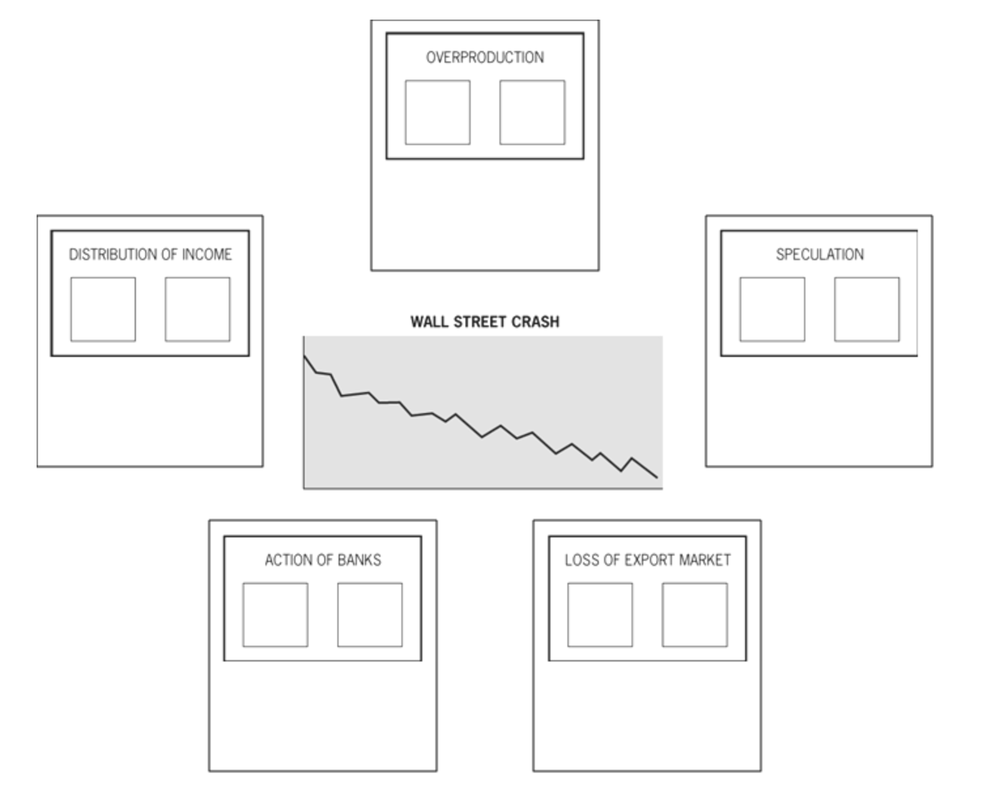
Again reading 211-212, complete the causes of the Wall Street Crash diagram (right). Add a brief note beneath each factor to explain how it helped to cause the Crash.
In one of the smaller boxes under each factor, put a letter to show what kind of cause it was: S short-term (arose in the weeks or months before the crash); L long-term (had been brewing up for years or even decades). In the other box, give the factor a mark out of 10 for its importance. Finally, you are an economic advisor employed to advise on reforming the US financial system. What practical changes would you suggest in order to prevent another Wall Street crash? |
The human cost of the Great Depression.
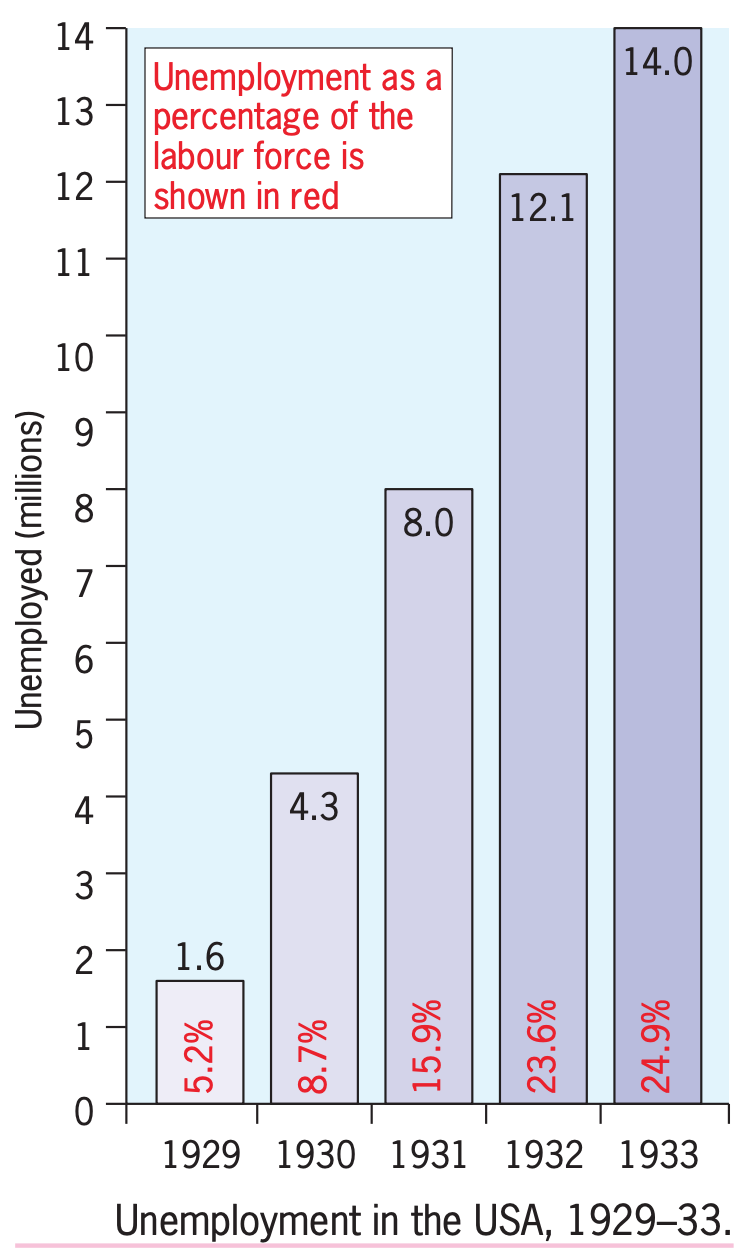
- Mass unemployment: One of the most devastating consequences of the Great Depression was the high level of unemployment. Millions of people lost their jobs as a result of the economic downturn, and many were unable to find work for years. Unemployment rates reached as high as 25% in some countries.
- Poverty: The Great Depression led to widespread poverty as people struggled to afford the basic necessities of life. Many people were unable to afford food, housing, and medical care, and they were forced to rely on government assistance or charity.
- Homelessness: The Great Depression led to an increase in homelessness as people were unable to afford housing. Many people lived in overcrowded or substandard housing, or they were forced to live in shelters or on the streets.
- Social unrest: The Great Depression led to social unrest and political turmoil in many countries. Protests and strikes were common as people demanded jobs and better living conditions. In some countries, the economic downturn led to the rise of extremist political movements.
- Bank failures: Many banks failed during the Great Depression, which led to a loss of savings for millions of people. The failure of banks also led to a loss of confidence in the banking system, which made it difficult for the economy to recover.
- Agricultural distress: The great depression hit hard on farmers, as agricultural prices fell significantly and it was difficult to sell their goods. Many farmers lost their land as they could not afford to pay their mortgages.
- Impact on mental health: The Great depression led to an increase in mental health problems, such as depression and suicide as people struggled to cope with unemployment, poverty, and hopelessness.
|
|
Lovely short film on Dorothea Lange's photography and BBC article about the 2023-24 US National Gallery of Art exhibition. NB The Matu examiners like her work.
Activity 3
Read the sources on pages 214 and 215 of your text book and consider the sources above. Make a set of notes that examines the human cost of the Depression by explaining both the impact on the rural and industrial communities of the USA. Activity 4 True or false quiz. 20 factual knowledge questions based on your understanding of this topic and the Crash Course film. |