|
IB Paper 3 - Europe - Past Paper Questions - For Inessa
This is the higher level essay paper, 18 sections, 36 possible questions. You choose three sections and write one essay on each. You have 5 minutes reading time and the 150 minutes to write the three essays. Below are the question patterns for three of the most popular 20th century questions. |
Past Paper Questions
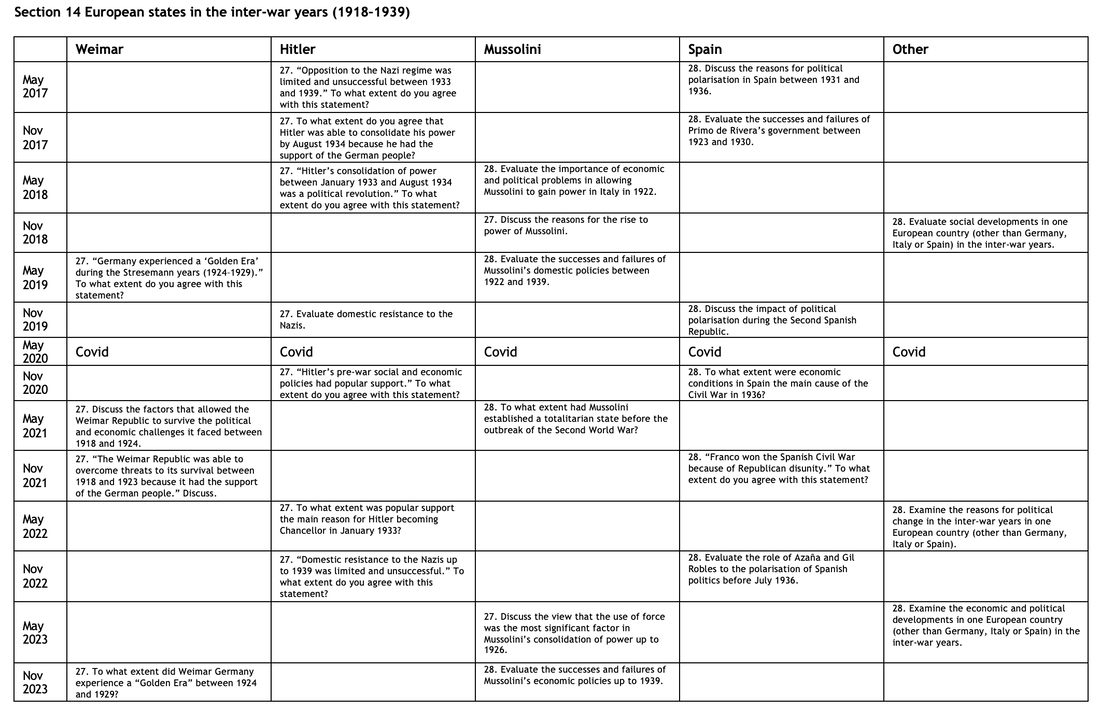
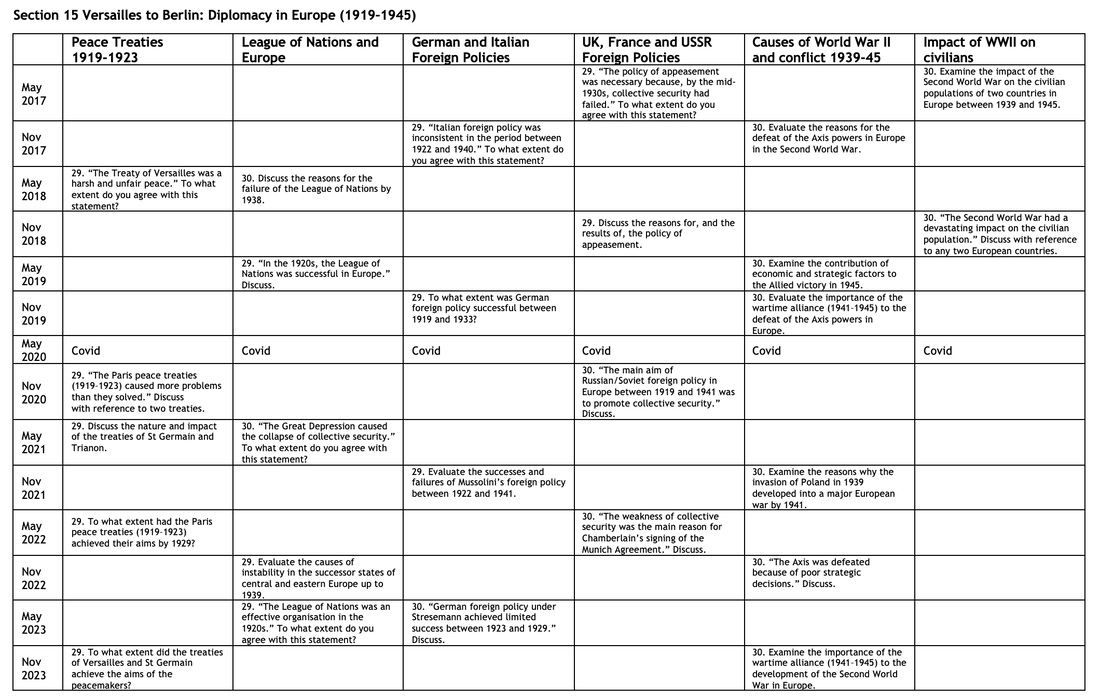
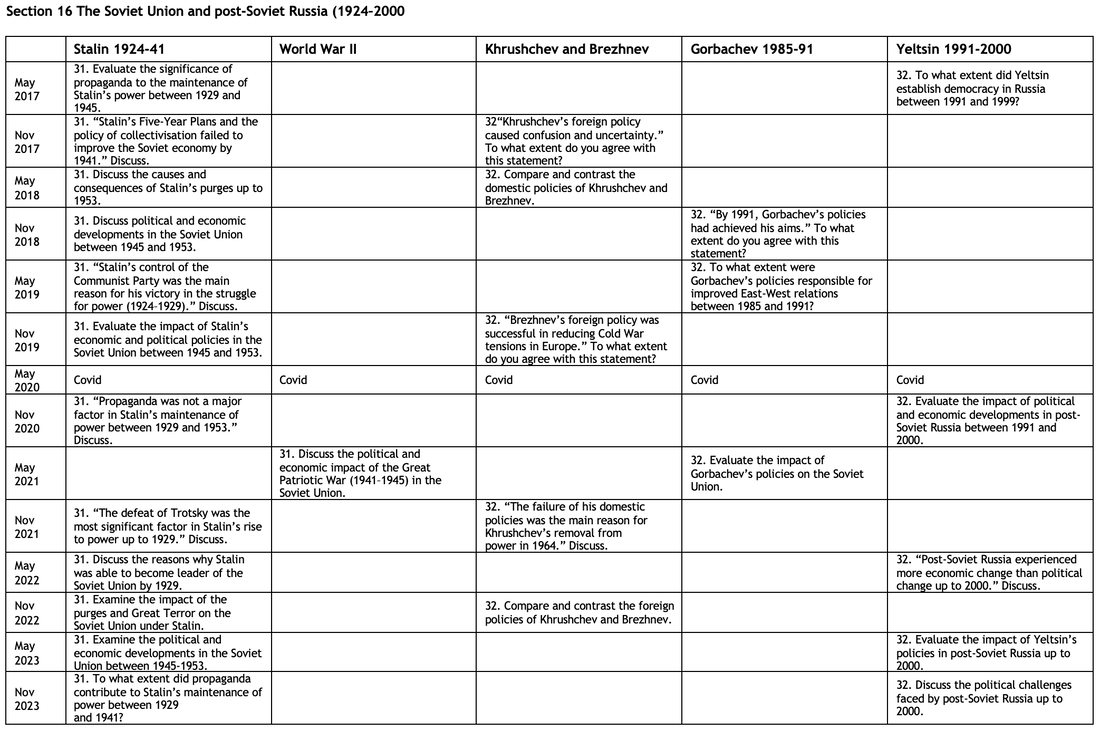
Although you have studied three areas of the syllabus, there are actually five sections that have essays that you might be able to attempt. Sections 17 and 18 dealing with Europe 1945-2000 have a degree of overlap with Paper 2. Click to enlarge.
Although you have studied three areas of the syllabus, there are actually five sections that have essays that you might be able to attempt. Sections 17 and 18 dealing with Europe 1945-2000 have a degree of overlap with Paper 2. Click to enlarge.
May 2017
Section 14 European states in the inter-war years (1918–1939)
27. “Opposition to the Nazi regime was limited and unsuccessful between 1933 and 1939.” To what extent do you agree with this statement?
28. Discuss the reasons for political polarisation in Spain between 1931 and 1936.
Section 15 Versailles to Berlin: Diplomacy in Europe (1919–1945)
29. “The policy of appeasement was necessary because, by the mid-1930s, collective security had failed.” To what extent do you agree with this statement?
30. Examine the impact of the Second World War on the civilian populations of two countries in Europe between 1939 and 1945.
Section 16 The Soviet Union and post-Soviet Russia (1924–2000)
31. Evaluate the significance of propaganda to the maintenance of Stalin’s power between 1929 and 1945.
32. To what extent did Yeltsin establish democracy in Russia between 1991 and 1999?
Section 17 Post-war western and northern Europe (1945–2000)
33. Discuss the role of de Gaulle in stabilising France between 1958 and 1969.
34. To what extent was there social and cultural change in West Germany between 1949 and 1989?
Section 18 Post-war central and eastern Europe (1945–2000)
35. Evaluate Yugoslavia’s challenge to Soviet control under Tito.
36. Between 1945 and 1968, to what extent was there support for Soviet control within two of the following: East Germany; Poland; Hungary; Czechoslovakia?
November 2017
Section 14 European states in the inter-war years (1918–1939)
27. To what extent do you agree that Hitler was able to consolidate his power by August 1934 because he had the support of the German people?
28. Evaluate the successes and failures of Primo de Rivera’s government between 1923 and 1930.
Section 15 Versailles to Berlin: Diplomacy in Europe (1919–1945)
29. “Italian foreign policy was inconsistent in the period between 1922 and 1940.” To what extent do you agree with this statement?
30. Evaluate the reasons for the defeat of the Axis powers in Europe in the Second World War.
Section 16 The Soviet Union and post-Soviet Russia (1924–2000)
31. “Stalin’s Five-Year Plans and the policy of collectivisation failed to improve the Soviet economy by 1941.” Discuss.
32“Khrushchev’s foreign policy caused confusion and uncertainty.” To what extent do you agree with this statement?
Section 17 Post-war western and northern Europe (1945–2000)
33. Evaluate the reasons for the emergence of the Cold War by 1949.
34. “Kohl’s support for the rapid reunification of Germany was motivated by political opportunism.” To what extent do you agree with this statement?
Section 18 Post-war central and eastern Europe (1945–2000)
35. Evaluate the impact of COMECON and the Warsaw Pact on states dominated by the Soviet Union.
36. Evaluate the developments in one central or eastern European country, excluding Russia, following the collapse of Soviet control.
May 2018
Section 14: European states in the inter-war years (1918–1939)
27. “Hitler’s consolidation of power between January 1933 and August 1934 was a political revolution.” To what extent do you agree with this statement?
28. Evaluate the importance of economic and political problems in allowing Mussolini to gain power in Italy in 1922.
Section 15: Versailles to Berlin: Diplomacy in Europe (1919–1945)
29. “The Treaty of Versailles was a harsh and unfair peace.” To what extent do you agree with this statement?
30. Discuss the reasons for the failure of the League of Nations by 1938.
Section 16: The Soviet Union and post-Soviet Russia (1924–2000)
31. Discuss the causes and consequences of Stalin’s purges up to 1953.
32. Compare and contrast the domestic policies of Khrushchev and Brezhnev.
Section 17: Post-war western and northern Europe (1945–2000)
33. With reference to the period up to 1949, evaluate the contribution of economic factors to the division of Germany.
34. Discuss the extent of political change in one western or northern European country (other than France, the Federal Republic of Germany and Spain) between 1945 and 2000.
Section 18: Post-war central and eastern Europe (1945–2000)
35. “Protests against Soviet domination in central and eastern Europe were unsuccessful up to 1980.” With reference to East Germany and Poland or Hungary and Czechoslovakia, to what extent do you agree with this statement?
36. Compare and contrast the role of Walesa in Poland and Havel in Czechoslovakia.
November 2018
Section 14: European states in the inter-war years (1918–1939)
27. Discuss the reasons for the rise to power of Mussolini.
28. Evaluate social developments in one European country (other than Germany, Italy or Spain) in the inter-war years.
Section 15: Versailles to Berlin: Diplomacy in Europe (1919–1945)
29. Discuss the reasons for, and the results of, the policy of appeasement.
30. “The Second World War had a devastating impact on the civilian population.” Discuss with reference to any two European countries.
Section 16: The Soviet Union and post-Soviet Russia (1924–2000)
31. Discuss political and economic developments in the Soviet Union between 1945 and 1953.
32. “By 1991, Gorbachev’s policies had achieved his aims.” To what extent do you agree with this statement?
Section 17: Post-war western and northern Europe (1945–2000)
33. Evaluate the role of Adenauer in Germany’s economic recovery.
34. Examine the role of Juan Carlos in Spain’s peaceful transition to democracy.
Section 18: Post-war central and eastern Europe (1945–2000)
35. Discuss the political and economic measures undertaken by the Soviet Union to dominate central and eastern Europe between 1945 and 1955.
36. Discuss the reasons for, and the results of, the uprising in Czechoslovakia (1968).
May 2019
Section 14: European states in the inter-war years (1918–1939)
27. “Germany experienced a ‘Golden Era’ during the Stresemann years (1924–1929).” To what extent do you agree with this statement?
28. Evaluate the successes and failures of Mussolini’s domestic policies between 1922 and 1939.
Section 15: Versailles to Berlin: Diplomacy in Europe (1919–1945)
29. “In the 1920s, the League of Nations was successful in Europe.” Discuss.
30. Examine the contribution of economic and strategic factors to the Allied victory in 1945.
Section 16: The Soviet Union and post-Soviet Russia (1924–2000)
31. “Stalin’s control of the Communist Party was the main reason for his victory in the struggle for power (1924–1929).” Discuss.
32. To what extent were Gorbachev’s policies responsible for improved East-West relations between 1985 and 1991?
November 2019
Section 14: European states in the inter-war years (1918–1939)
27. Evaluate domestic resistance to the Nazis.
28. Discuss the impact of political polarisation during the Second Spanish Republic.
Section 15: Versailles to Berlin: Diplomacy in Europe (1919–1945)
29. To what extent was German foreign policy successful between 1919 and 1933?
30. Evaluate the importance of the wartime alliance (1941–1945) to the defeat of the Axis powers in Europe.
Section 16: The Soviet Union and post-Soviet Russia (1924–2000)
31. Evaluate the impact of Stalin’s economic and political policies in the Soviet Union between 1945 and 1953.
32. “Brezhnev’s foreign policy was successful in reducing Cold War tensions in Europe.” To what extent do you agree with this statement?
November 2020
Section 14: Inter-war domestic developments in European states (1918–1939)
27. “Hitler’s pre-war social and economic policies had popular support.” To what extent do you agree with this statement?
28. To what extent were economic conditions in Spain the main cause of the Civil War in 1936?
Section 15: Diplomacy in Europe (1919–1945)
29. “The Paris peace treaties (1919–1923) caused more problems than they solved.” Discuss
with reference to two treaties.
30. “The main aim of Russian/Soviet foreign policy in Europe between 1919 and 1941 was to promote collective security.” Discuss.
Section 16: The Soviet Union and post-Soviet Russia (1924–2000)
31. “Propaganda was not a major factor in Stalin’s maintenance of power between 1929 and 1953.” Discuss.
32. Evaluate the impact of political and economic developments in post-Soviet Russia between 1991 and 2000.
May 2021
Section 14: Inter-war domestic developments in European states (1918–1939)
27. Discuss the factors that allowed the Weimar Republic to survive the political and economic challenges it faced between 1918 and 1924.
28. To what extent had Mussolini established a totalitarian state before the outbreak of the Second World War?
Section 15: Diplomacy in Europe (1919–1945)
29. Discuss the nature and impact of the treaties of St Germain and Trianon.
30. “The Great Depression caused the collapse of collective security.” To what extent do you agree with this statement?
Section 16: The Soviet Union and post-Soviet Russia (1924–2000)
31. Discuss the political and economic impact of the Great Patriotic War (1941–1945) in the Soviet Union.
32. Evaluate the impact of Gorbachev’s policies on the Soviet Union.
November 2021
Section 14: Inter-war domestic developments in European states (1918–1939)
27. “The Weimar Republic was able to overcome threats to its survival between 1918 and 1923
because it had the support of the German people.” Discuss.
28. “Franco won the Spanish Civil War because of Republican disunity.” To what extent do you agree with this statement?
Section 15: Diplomacy in Europe (1919–1945)
29. Evaluate the successes and failures of Mussolini’s foreign policy between 1922 and 1941.
30. Examine the reasons why the invasion of Poland in 1939 developed into a major European
war by 1941.
Section 16: The Soviet Union and post-Soviet Russia (1924–2000)
31. “The defeat of Trotsky was the most significant factor in Stalin’s rise to power up to 1929.” Discuss.
32. “The failure of his domestic policies was the main reason for Khrushchev’s removal from
power in 1964.” Discuss.
Section 17: Post-war western and northern Europe (1945–2000)
33. Evaluate the political responses to post-war economic challenges in France up to 1963.
34. With reference to the period 1949–1990, examine the impact of social and cultural change in West Germany.
May 2022
Section 14: Inter-war domestic developments in European states (1918–1939)
27. To what extent was popular support the main reason for Hitler becoming Chancellor in January 1933?
28. Examine the reasons for political change in the inter-war years in one European country (other than Germany, Italy or Spain).
Section 15: Diplomacy in Europe (1919–1945)
29. To what extent had the Paris peace treaties (1919–1923) achieved their aims by 1929?
30. “The weakness of collective security was the main reason for Chamberlain’s signing of the Munich Agreement.” Discuss.
Section 16: The Soviet Union and post-Soviet Russia (1924–2000)
31. Discuss the reasons why Stalin was able to become leader of the Soviet Union by 1929.
32. “Post-Soviet Russia experienced more economic change than political change up to 2000.” Discuss.
Section 17: Post-war western and northern Europe (1945–2000)
33. “The state played the most significant role in achieving economic recovery during
‘Les Trente Glorieuses’ in France.” Discuss.
34. Evaluate the social changes in one western or northern European country (other than France, the Federal Republic of Germany and Spain) between 1945–2000.
Section 18: Post-war central and eastern Europe (1945–2000)
35. “Repression was the main reason for Soviet domination between 1945 and 1968.” Discuss with reference to two of the following countries: East Germany, Poland, Hungary, Czechoslovakia.
36. Examine the social and economic challenges faced by one country in central or eastern Europe from 1989 to 2000.
November 2022
Section 14: Inter-war domestic developments in European states (1918–1939)
27. “Domestic resistance to the Nazis up to 1939 was limited and unsuccessful.” To what extent do you agree with this statement?
28. Evaluate the role of Azaña and Gil Robles to the polarisation of Spanish politics before July 1936.
Section 15: Diplomacy in Europe (1919–1945)
29. Evaluate the causes of instability in the successor states of central and eastern Europe up to 1939.
30. “The Axis was defeated because of poor strategic decisions.” Discuss.
Section 16: The Soviet Union and post-Soviet Russia (1924–2000)
31. Examine the impact of the purges and Great Terror on the Soviet Union under Stalin.
32. Compare and contrast the foreign policies of Khrushchev and Brezhnev.
Section 17: Post-war western and northern Europe (1945–2000)
33. “Debt was the most significant post-war problem in Western Europe.” Discuss with reference to either France or West Germany.
34. Examine the challenges to the establishment of democracy in Spain under Juan Carlos up to 1982.
Section 18: Post-war central and eastern Europe (1945–2000)
35. Evaluate the factors leading to the collapse of Soviet control in central and eastern Europe.
36. Discuss the role played by Milošević in the Balkan conflicts in the 1990s.
May 2023
Section 14: Inter-war domestic developments in European states (1918-1939)
27. Discuss the view that the use of force was the most significant factor in Mussolini’s consolidation of power up to 1926.
28. Examine the economic and political developments in one European country (other than Germany, Italy or Spain) in the inter-war years.
Section 15: Diplomacy in Europe (1919-1945)
29. “The League of Nations was an effective organisation in the 1920s.” To what extent do you agree with this statement?
30. “German foreign policy under Stresemann achieved limited success between 1923 and 1929.” Discuss.
Section 16: The Soviet Union and post-Soviet Russia (1924-2000)
31. Examine the political and economic developments in the Soviet Union between 1945-1953.
32. Evaluate the impact of Yeltsin’s policies in post-Soviet Russia up to 2000.
Section 17: Post-war western and northern Europe (1945-2000)
33. “Fear of the spread of communism led to the breakdown of the wartime alliance in Europe.” Discuss.
34. Discuss the factors that contributed to the German “economic miracle” up to 1963.
Section 18: Post-war central and eastern Europe (1945-2000)
35. To what extent were economic factors the main motive for Soviet domination in central and eastern Europe between 1945-1955?
36. Examine the consequences of the collapse of Soviet control in central and eastern Europe.
November 2023
Section 14: Inter-war domestic developments in European states (1918–1939)
27. To what extent did Weimar Germany experience a “Golden Era” between 1924 and 1929?
28. Evaluate the successes and failures of Mussolini’s economic policies up to 1939.
Section 15: Diplomacy in Europe (1919–1945)
29. To what extent did the treaties of Versailles and St Germain achieve the aims of the peacemakers?
30. Examine the importance of the wartime alliance (1941–1945) to the development of the
Second World War in Europe.
Section 16: The Soviet Union and post-Soviet Russia (1924–2000)
31. To what extent did propaganda contribute to Stalin’s maintenance of power between 1929
and 1941?
32. Discuss the political challenges faced by post-Soviet Russia up to 2000.
Section 17: Post-war western and northern Europe (1945–2000)
33. Evaluate the successes and failures of Kohl´s policies up to the end of 1990.
34. Evaluate the extent of social and economic change in one western or northern European
country (other than France, the Federal Republic of Germany and Spain) between 1945 and 2000.
Section 18: Post-war central and eastern Europe (1945–2000)
35. Discuss the view that Tito’s leadership was the main reason for Yugoslavia’s successful
challenge to Soviet control.
36. “Ethnic disputes were the main cause of the Balkan conflicts in the 1990s.” Discuss.
Section 14 European states in the inter-war years (1918–1939)
27. “Opposition to the Nazi regime was limited and unsuccessful between 1933 and 1939.” To what extent do you agree with this statement?
28. Discuss the reasons for political polarisation in Spain between 1931 and 1936.
Section 15 Versailles to Berlin: Diplomacy in Europe (1919–1945)
29. “The policy of appeasement was necessary because, by the mid-1930s, collective security had failed.” To what extent do you agree with this statement?
30. Examine the impact of the Second World War on the civilian populations of two countries in Europe between 1939 and 1945.
Section 16 The Soviet Union and post-Soviet Russia (1924–2000)
31. Evaluate the significance of propaganda to the maintenance of Stalin’s power between 1929 and 1945.
32. To what extent did Yeltsin establish democracy in Russia between 1991 and 1999?
Section 17 Post-war western and northern Europe (1945–2000)
33. Discuss the role of de Gaulle in stabilising France between 1958 and 1969.
34. To what extent was there social and cultural change in West Germany between 1949 and 1989?
Section 18 Post-war central and eastern Europe (1945–2000)
35. Evaluate Yugoslavia’s challenge to Soviet control under Tito.
36. Between 1945 and 1968, to what extent was there support for Soviet control within two of the following: East Germany; Poland; Hungary; Czechoslovakia?
November 2017
Section 14 European states in the inter-war years (1918–1939)
27. To what extent do you agree that Hitler was able to consolidate his power by August 1934 because he had the support of the German people?
28. Evaluate the successes and failures of Primo de Rivera’s government between 1923 and 1930.
Section 15 Versailles to Berlin: Diplomacy in Europe (1919–1945)
29. “Italian foreign policy was inconsistent in the period between 1922 and 1940.” To what extent do you agree with this statement?
30. Evaluate the reasons for the defeat of the Axis powers in Europe in the Second World War.
Section 16 The Soviet Union and post-Soviet Russia (1924–2000)
31. “Stalin’s Five-Year Plans and the policy of collectivisation failed to improve the Soviet economy by 1941.” Discuss.
32“Khrushchev’s foreign policy caused confusion and uncertainty.” To what extent do you agree with this statement?
Section 17 Post-war western and northern Europe (1945–2000)
33. Evaluate the reasons for the emergence of the Cold War by 1949.
34. “Kohl’s support for the rapid reunification of Germany was motivated by political opportunism.” To what extent do you agree with this statement?
Section 18 Post-war central and eastern Europe (1945–2000)
35. Evaluate the impact of COMECON and the Warsaw Pact on states dominated by the Soviet Union.
36. Evaluate the developments in one central or eastern European country, excluding Russia, following the collapse of Soviet control.
May 2018
Section 14: European states in the inter-war years (1918–1939)
27. “Hitler’s consolidation of power between January 1933 and August 1934 was a political revolution.” To what extent do you agree with this statement?
28. Evaluate the importance of economic and political problems in allowing Mussolini to gain power in Italy in 1922.
Section 15: Versailles to Berlin: Diplomacy in Europe (1919–1945)
29. “The Treaty of Versailles was a harsh and unfair peace.” To what extent do you agree with this statement?
30. Discuss the reasons for the failure of the League of Nations by 1938.
Section 16: The Soviet Union and post-Soviet Russia (1924–2000)
31. Discuss the causes and consequences of Stalin’s purges up to 1953.
32. Compare and contrast the domestic policies of Khrushchev and Brezhnev.
Section 17: Post-war western and northern Europe (1945–2000)
33. With reference to the period up to 1949, evaluate the contribution of economic factors to the division of Germany.
34. Discuss the extent of political change in one western or northern European country (other than France, the Federal Republic of Germany and Spain) between 1945 and 2000.
Section 18: Post-war central and eastern Europe (1945–2000)
35. “Protests against Soviet domination in central and eastern Europe were unsuccessful up to 1980.” With reference to East Germany and Poland or Hungary and Czechoslovakia, to what extent do you agree with this statement?
36. Compare and contrast the role of Walesa in Poland and Havel in Czechoslovakia.
November 2018
Section 14: European states in the inter-war years (1918–1939)
27. Discuss the reasons for the rise to power of Mussolini.
28. Evaluate social developments in one European country (other than Germany, Italy or Spain) in the inter-war years.
Section 15: Versailles to Berlin: Diplomacy in Europe (1919–1945)
29. Discuss the reasons for, and the results of, the policy of appeasement.
30. “The Second World War had a devastating impact on the civilian population.” Discuss with reference to any two European countries.
Section 16: The Soviet Union and post-Soviet Russia (1924–2000)
31. Discuss political and economic developments in the Soviet Union between 1945 and 1953.
32. “By 1991, Gorbachev’s policies had achieved his aims.” To what extent do you agree with this statement?
Section 17: Post-war western and northern Europe (1945–2000)
33. Evaluate the role of Adenauer in Germany’s economic recovery.
34. Examine the role of Juan Carlos in Spain’s peaceful transition to democracy.
Section 18: Post-war central and eastern Europe (1945–2000)
35. Discuss the political and economic measures undertaken by the Soviet Union to dominate central and eastern Europe between 1945 and 1955.
36. Discuss the reasons for, and the results of, the uprising in Czechoslovakia (1968).
May 2019
Section 14: European states in the inter-war years (1918–1939)
27. “Germany experienced a ‘Golden Era’ during the Stresemann years (1924–1929).” To what extent do you agree with this statement?
28. Evaluate the successes and failures of Mussolini’s domestic policies between 1922 and 1939.
Section 15: Versailles to Berlin: Diplomacy in Europe (1919–1945)
29. “In the 1920s, the League of Nations was successful in Europe.” Discuss.
30. Examine the contribution of economic and strategic factors to the Allied victory in 1945.
Section 16: The Soviet Union and post-Soviet Russia (1924–2000)
31. “Stalin’s control of the Communist Party was the main reason for his victory in the struggle for power (1924–1929).” Discuss.
32. To what extent were Gorbachev’s policies responsible for improved East-West relations between 1985 and 1991?
November 2019
Section 14: European states in the inter-war years (1918–1939)
27. Evaluate domestic resistance to the Nazis.
28. Discuss the impact of political polarisation during the Second Spanish Republic.
Section 15: Versailles to Berlin: Diplomacy in Europe (1919–1945)
29. To what extent was German foreign policy successful between 1919 and 1933?
30. Evaluate the importance of the wartime alliance (1941–1945) to the defeat of the Axis powers in Europe.
Section 16: The Soviet Union and post-Soviet Russia (1924–2000)
31. Evaluate the impact of Stalin’s economic and political policies in the Soviet Union between 1945 and 1953.
32. “Brezhnev’s foreign policy was successful in reducing Cold War tensions in Europe.” To what extent do you agree with this statement?
November 2020
Section 14: Inter-war domestic developments in European states (1918–1939)
27. “Hitler’s pre-war social and economic policies had popular support.” To what extent do you agree with this statement?
28. To what extent were economic conditions in Spain the main cause of the Civil War in 1936?
Section 15: Diplomacy in Europe (1919–1945)
29. “The Paris peace treaties (1919–1923) caused more problems than they solved.” Discuss
with reference to two treaties.
30. “The main aim of Russian/Soviet foreign policy in Europe between 1919 and 1941 was to promote collective security.” Discuss.
Section 16: The Soviet Union and post-Soviet Russia (1924–2000)
31. “Propaganda was not a major factor in Stalin’s maintenance of power between 1929 and 1953.” Discuss.
32. Evaluate the impact of political and economic developments in post-Soviet Russia between 1991 and 2000.
May 2021
Section 14: Inter-war domestic developments in European states (1918–1939)
27. Discuss the factors that allowed the Weimar Republic to survive the political and economic challenges it faced between 1918 and 1924.
28. To what extent had Mussolini established a totalitarian state before the outbreak of the Second World War?
Section 15: Diplomacy in Europe (1919–1945)
29. Discuss the nature and impact of the treaties of St Germain and Trianon.
30. “The Great Depression caused the collapse of collective security.” To what extent do you agree with this statement?
Section 16: The Soviet Union and post-Soviet Russia (1924–2000)
31. Discuss the political and economic impact of the Great Patriotic War (1941–1945) in the Soviet Union.
32. Evaluate the impact of Gorbachev’s policies on the Soviet Union.
November 2021
Section 14: Inter-war domestic developments in European states (1918–1939)
27. “The Weimar Republic was able to overcome threats to its survival between 1918 and 1923
because it had the support of the German people.” Discuss.
28. “Franco won the Spanish Civil War because of Republican disunity.” To what extent do you agree with this statement?
Section 15: Diplomacy in Europe (1919–1945)
29. Evaluate the successes and failures of Mussolini’s foreign policy between 1922 and 1941.
30. Examine the reasons why the invasion of Poland in 1939 developed into a major European
war by 1941.
Section 16: The Soviet Union and post-Soviet Russia (1924–2000)
31. “The defeat of Trotsky was the most significant factor in Stalin’s rise to power up to 1929.” Discuss.
32. “The failure of his domestic policies was the main reason for Khrushchev’s removal from
power in 1964.” Discuss.
Section 17: Post-war western and northern Europe (1945–2000)
33. Evaluate the political responses to post-war economic challenges in France up to 1963.
34. With reference to the period 1949–1990, examine the impact of social and cultural change in West Germany.
May 2022
Section 14: Inter-war domestic developments in European states (1918–1939)
27. To what extent was popular support the main reason for Hitler becoming Chancellor in January 1933?
28. Examine the reasons for political change in the inter-war years in one European country (other than Germany, Italy or Spain).
Section 15: Diplomacy in Europe (1919–1945)
29. To what extent had the Paris peace treaties (1919–1923) achieved their aims by 1929?
30. “The weakness of collective security was the main reason for Chamberlain’s signing of the Munich Agreement.” Discuss.
Section 16: The Soviet Union and post-Soviet Russia (1924–2000)
31. Discuss the reasons why Stalin was able to become leader of the Soviet Union by 1929.
32. “Post-Soviet Russia experienced more economic change than political change up to 2000.” Discuss.
Section 17: Post-war western and northern Europe (1945–2000)
33. “The state played the most significant role in achieving economic recovery during
‘Les Trente Glorieuses’ in France.” Discuss.
34. Evaluate the social changes in one western or northern European country (other than France, the Federal Republic of Germany and Spain) between 1945–2000.
Section 18: Post-war central and eastern Europe (1945–2000)
35. “Repression was the main reason for Soviet domination between 1945 and 1968.” Discuss with reference to two of the following countries: East Germany, Poland, Hungary, Czechoslovakia.
36. Examine the social and economic challenges faced by one country in central or eastern Europe from 1989 to 2000.
November 2022
Section 14: Inter-war domestic developments in European states (1918–1939)
27. “Domestic resistance to the Nazis up to 1939 was limited and unsuccessful.” To what extent do you agree with this statement?
28. Evaluate the role of Azaña and Gil Robles to the polarisation of Spanish politics before July 1936.
Section 15: Diplomacy in Europe (1919–1945)
29. Evaluate the causes of instability in the successor states of central and eastern Europe up to 1939.
30. “The Axis was defeated because of poor strategic decisions.” Discuss.
Section 16: The Soviet Union and post-Soviet Russia (1924–2000)
31. Examine the impact of the purges and Great Terror on the Soviet Union under Stalin.
32. Compare and contrast the foreign policies of Khrushchev and Brezhnev.
Section 17: Post-war western and northern Europe (1945–2000)
33. “Debt was the most significant post-war problem in Western Europe.” Discuss with reference to either France or West Germany.
34. Examine the challenges to the establishment of democracy in Spain under Juan Carlos up to 1982.
Section 18: Post-war central and eastern Europe (1945–2000)
35. Evaluate the factors leading to the collapse of Soviet control in central and eastern Europe.
36. Discuss the role played by Milošević in the Balkan conflicts in the 1990s.
May 2023
Section 14: Inter-war domestic developments in European states (1918-1939)
27. Discuss the view that the use of force was the most significant factor in Mussolini’s consolidation of power up to 1926.
28. Examine the economic and political developments in one European country (other than Germany, Italy or Spain) in the inter-war years.
Section 15: Diplomacy in Europe (1919-1945)
29. “The League of Nations was an effective organisation in the 1920s.” To what extent do you agree with this statement?
30. “German foreign policy under Stresemann achieved limited success between 1923 and 1929.” Discuss.
Section 16: The Soviet Union and post-Soviet Russia (1924-2000)
31. Examine the political and economic developments in the Soviet Union between 1945-1953.
32. Evaluate the impact of Yeltsin’s policies in post-Soviet Russia up to 2000.
Section 17: Post-war western and northern Europe (1945-2000)
33. “Fear of the spread of communism led to the breakdown of the wartime alliance in Europe.” Discuss.
34. Discuss the factors that contributed to the German “economic miracle” up to 1963.
Section 18: Post-war central and eastern Europe (1945-2000)
35. To what extent were economic factors the main motive for Soviet domination in central and eastern Europe between 1945-1955?
36. Examine the consequences of the collapse of Soviet control in central and eastern Europe.
November 2023
Section 14: Inter-war domestic developments in European states (1918–1939)
27. To what extent did Weimar Germany experience a “Golden Era” between 1924 and 1929?
28. Evaluate the successes and failures of Mussolini’s economic policies up to 1939.
Section 15: Diplomacy in Europe (1919–1945)
29. To what extent did the treaties of Versailles and St Germain achieve the aims of the peacemakers?
30. Examine the importance of the wartime alliance (1941–1945) to the development of the
Second World War in Europe.
Section 16: The Soviet Union and post-Soviet Russia (1924–2000)
31. To what extent did propaganda contribute to Stalin’s maintenance of power between 1929
and 1941?
32. Discuss the political challenges faced by post-Soviet Russia up to 2000.
Section 17: Post-war western and northern Europe (1945–2000)
33. Evaluate the successes and failures of Kohl´s policies up to the end of 1990.
34. Evaluate the extent of social and economic change in one western or northern European
country (other than France, the Federal Republic of Germany and Spain) between 1945 and 2000.
Section 18: Post-war central and eastern Europe (1945–2000)
35. Discuss the view that Tito’s leadership was the main reason for Yugoslavia’s successful
challenge to Soviet control.
36. “Ethnic disputes were the main cause of the Balkan conflicts in the 1990s.” Discuss.